User:ApeKattQuest, MonkeyPython/v*na: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
kashmir (saran)<br> |
kashmir (saran)<br> |
||
south afghanistan (sarang)<br> |
south afghanistan (sarang)<br> |
||
jammu (saranga)<br>< |
jammu (saranga)<br></td> |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | .type of lute, evolved from the rabab includes this and the ghaychak [https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q1521728 wd] [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ghaychak en] [https://musicbrainz.org/instrument/d50ba107-4930-4e0b-8b3f-ffbea4a1ade1 mb] [https://tickets.metabrainz.org/browse/INST-371 jira]< |
||
< |
<tr> |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
<td> in its family evolved from the kobyz [https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q1778051 wd] [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kobyz en] [https://tickets.metabrainz.org/browse/INST-439 jira]. (kobyz, ghaychak, sarangi)<br></td> |
|||
<td>Cell 2</td> |
|||
</tr> |
</tr> |
||
<tr> |
<tr> |
||
| Line 68: | Line 72: | ||
<td>https://saisaibatake.ame-zaiku.com/musical/instruments/sursringar_i.jpg</td> |
<td>https://saisaibatake.ame-zaiku.com/musical/instruments/sursringar_i.jpg</td> |
||
</tr> |
</tr> |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
<td>Cell 2</td> |
<td>Cell 2</td> |
||
</tr> |
</tr> |
||
<td> |
<td>taus mayerivina<br></td> |
||
<td>Cell 2</td> |
<td>Cell 2</td> |
||
</tr> |
</tr> |
||
<td> |
<td>dhodro banam |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
<td>Cell 2</td> |
<td>Cell 2</td> |
||
</tr> |
</tr> |
||
<td> |
<td>bin-sitar</td> |
||
<td>Cell 2</td> |
<td>Cell 2</td> |
||
</tr> |
</tr> |
||
<td> |
<td>kamaica</td> |
||
<td>Cell 2</td> |
<td>Cell 2</td> |
||
</tr> |
</tr> |
||
<td> |
<td>ravanhattha</td> |
||
<td>Cell 2</td> |
<td>Cell 2</td> |
||
</tr> |
</tr> |
||
<td> |
<td>khuur (mongolian fiddles)</td> |
||
<td>Cell 2</td> |
<td>Cell 2</td> |
||
</tr> |
</tr> |
||
| Line 99: | Line 105: | ||
.....<br> |
.....<br> |
||
| ⚫ | |||
<br> |
|||
<br> |
|||
<br> |
|||
<br> |
|||
<br> |
|||
+ lookup +<br> |
|||
taus mayerivina<br> |
|||
veena<br> |
|||
dhodro banam<br> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
bin-sitar<br> |
|||
kamaica<br> |
|||
ravanhattha<br> |
|||
khuur (mongolian fiddles)<br> |
|||
<br> |
<br> |
||
<br> |
<br> |
||
| ⚫ | |||
<br> |
<br> |
||
<br> |
<br> |
||
| Line 127: | Line 113: | ||
suba<br> |
suba<br> |
||
sita<br> |
sita<br> |
||
Origin: India, 13th century.<br> |
|||
Strings/Courses: 7/7<br> |
|||
Further notes: 3 drone strings, 5 melody strings, usually 12 sympathetic strings. Sympathetic strings are tuned depending on the raga being played. Steel strings.<br> |
|||
Scale Length: 680-870mm<br> |
|||
<br> |
|||
The Sitar is a Hindustani Classical Instrument. <br> |
|||
saro<br> |
saro<br> |
||
sari<br> |
sari<br> |
||
| Line 140: | Line 120: | ||
'''rabab'''-> sarod<br> |
'''rabab'''-> sarod<br> |
||
<br> |
<br> |
||
How many r*b*b's do we have?:<br> |
|||
<br> |
|||
double chested '''rabab''' (pearshaped lute rubab)<br> |
|||
long-necked rabab (spikefiddle rebab)<br> |
|||
<br> |
|||
So:<br> |
|||
<br> |
|||
* spikefiddle, to wit the ghijak [https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q54995817 wd] [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ghijak en] [https://musicbrainz.org/instrument/0d766870-3021-47ce-bd51-78d2d2484e1b mb] and the [[User:CatCat/k*m*n*|kemenche]] belong... |
|||
* short necked fiddle boat-shaped (appears similar to double chested ones and may these pre-evolution) |
|||
* long necked barbed lute (pearshaped lutes?!) kamanche, ravaj, read vina |
|||
* double chested lutes, herein the sarinda and sarangi families. |
|||
<br> |
<br> |
||
https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/From-Tri-tantri-Veena-to-Sitar/articleshow/21391436.cms and images on https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tritantri_vina and https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Setar (compare image on https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sitar ) makes it clear that it is the setar that is evolved from the tritantri veena - the sitar https://beta.musicbrainz.org/instrument/9290b2c1-97c3-4355-a26f-c6dba89cf8ff/ an unrelated (but possible distant cousin) was *named* after the Persian setar. |
https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/From-Tri-tantri-Veena-to-Sitar/articleshow/21391436.cms and images on https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tritantri_vina and https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Setar (compare image on https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sitar ) makes it clear that it is the setar that is evolved from the tritantri veena - the sitar https://beta.musicbrainz.org/instrument/9290b2c1-97c3-4355-a26f-c6dba89cf8ff/ an unrelated (but possible distant cousin) was *named* after the Persian setar. |
||
Revision as of 12:47, 4 February 2020
Veena or vina
Veena:
| Cell 1 | Cell 2 |
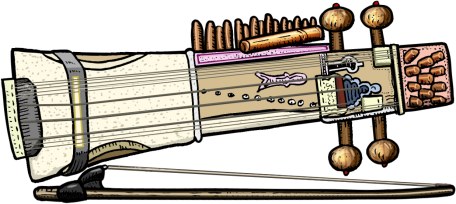
| sarangi wd en mb hindustani classical music, rajasthani folk sarangi, nepali sarangi wd en MB!(?) |
 |
| .type of lute, evolved from the rabab includes this and the ghaychak wd en mb jira | Cell 2 |
| in its family evolved from the kobyz wd en jira. (kobyz, ghaychak, sarangi) |
Cell 2 |
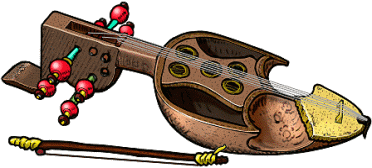
| sarinda wd en jira, is related to and may derive from central asian shamans-fiddle qobuz (kobys?) widespread:
rajasthan (surinda) three main strings
manipur north-east india (sananta) |
 |
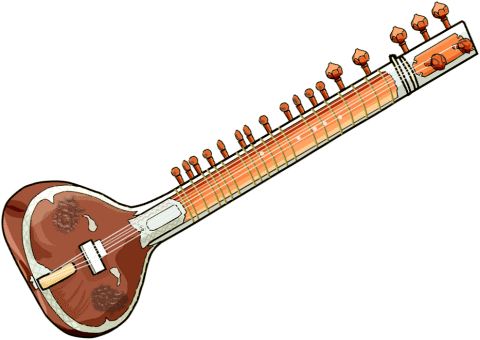
| sitar wd en mb hindustani sitar seems to have more in common with large uzbek dutar wd en mb than persian setar wd en mb
other sitar types: (distribution and related features suggest a common development)
sada sitar (plain or practice sitar) |
 |
| surbahar wd en mb effectively a bass sitar. invented c1820 by ghulam muhammad |
Cell 2 |
| Sursingar wd en mb hybrid plucked north indian classical lute invented c1800 by jaffar khan (seniya family) resonator, front and bridge from sitar, upperpart of neck/pegboard like the rabab, tuned and played like rabab, plectrum like sitar. |
 |
| svaraj fretless long necked plucked lute from bangladesj, it is a bangl version of the bengali/northindian dotara, it ought to be spelled saraj (see esraj) |
Cell 2 |
| taus mayerivina |
Cell 2 |
dhodro banam
|
Cell 2 |
| bin-sitar | Cell 2 |
| kamaica | Cell 2 |
| ravanhattha | Cell 2 |
| khuur (mongolian fiddles) | Cell 2 |
| Cell 1 | Cell 2 |
.....
sara
surs
suba
sita
saro
sari
banam(rebs)
rabab-> sarod
https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/From-Tri-tantri-Veena-to-Sitar/articleshow/21391436.cms and images on https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tritantri_vina and https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Setar (compare image on https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sitar ) makes it clear that it is the setar that is evolved from the tritantri veena - the sitar https://beta.musicbrainz.org/instrument/9290b2c1-97c3-4355-a26f-c6dba89cf8ff/ an unrelated (but possible distant cousin) was *named* after the Persian setar.